IoT Devices in Healthcare: Examples and Management Best Practices
IoT devices in healthcare enhance real-time monitoring, speed up treatment, automate critical processes, and improve patient outcomes. For example, connected devices like wearable fitness trackers and AI-powered diagnostic tools allow seamless communication between patients, physicians, and hospitals, supporting timely interventions and personalized care. Others, like IP cameras and badge readers, are designed to protect the physical premises of healthcare centers.
However, the increasing adoption of healthcare IoT creates security concerns because they are connected to the network and can be exploited by attackers.
This article explores several niche and general IoT devices in healthcare, some vulnerabilities that healthcare IoT devices are prone to, and best practices for protecting against these vulnerabilities.
Summary of key IoT devices in healthcare
| Smart wearables | Devices like wristbands, smartwatches, and smart rings that measure vital health and fitness metrics. |
| Smart sleeping equipment | Devices that measure and improve health vitals during sleep. |
| Glucose monitoring equipment | Devices that measure glucose levels, helping diabetics and athletes. |
| EKG at home | Devices that help people with cardiovascular conditions who require frequent EKGs. |
| Sleep assistant devices | Devices that help you sleep better through interventions like temperature and elevation adjustment. |
| Tremor therapy | Devices that help people with essential tremors or Parkinson’s disease get relief. |
| Pose correction devices | Devices that make the user mindful of an incorrect pose and encourage them to correct it. |
| Smart hearing aids | Upgrade of traditional hearing aids featuring capabilities like voice isolation, music mode, and noise-cancellation. |
| Robotic surgery | Ultra-high precision surgery with minimal human intervention. |
| Smart beds and accessories | Smart hospital beds monitor the patient’s vitals and alert the staff when necessary. Accessories like smart IV pumps help regulate drug dosages. |
| Smart imaging systems | Smart MRI, X-ray, and CT scan machines enable remote diagnosis by uploading images to the cloud and reducing imaging time with the help of AI. |
| Physical security equipment | CCTV cameras, access control systems, visitor management, and alarm systems help provide physical security to the hospital environment. |
Health and mood-monitoring devices
Smart wearables
This category includes wristbands, smart watches, smart rings, etc. These wearables come in all shapes and sizes and measure vital health and fitness parameters.
Reach Wrist Band by Silvertree is a device aimed at the elderly and other vulnerable groups that automatically detects falls and triggers an SOS signal to carers. Equipped with GPS and LTE connectivity, this wristband relays the patient’s live location to help care reach them sooner. The user can also manually trigger an SOS at the push of a button.

Reach Wristband (Source)
Motiv Ring monitors sleep patterns, heart rate, calories burned, and steps completed. It can share data with apps like Apple Health and Google Fit to centralize health management. Several competitors, such as Gabit, Oura, and Ultrahuman, also exist in this space.
-

Monitor the health of physical security devices and receive alerts in real-time
-

Automate firmware upgrades, password rotations & certificate management
-

Generate ad hoc and scheduled compliance reports
Smart sleeping equipment
Several products help customers measure and improve their sleep.
Sleep by Withings is an under-the-mattress accessory that performs sleep quality assessment, snoring detection, and heart rate tracking. It connects to the home WiFi and shares data with the Withings app.

Sleep (Source)
Ava Fertility is an innovative FDA-cleared product that tracks five physiological signals to detect five of the six most fertile days for a woman wanting to conceive. It must be used only while sleeping.
Glucose monitoring equipment
Diabetics or athletes who want to maintain specific glucose levels during peak exercise are typical target customers for this device category. An example device is Abbott’s Freestyle Libre. This device doesn’t prick and stays within the skin cells to provide continuous glucose monitoring for 14 days. The data is available on the Freestyle LibreLink app within 1 second of the device’s application. Another example is the Dexcom G7 Continuous Glucose Monitoring system.

Freestyle Libre (Source)
EKG at home
People with cardiovascular conditions frequently require EKGs (electrocardiograms) to measure the electrical activity of their heart. Portable smart devices are now available to help you take an EKG anywhere and deliver the report to your phone in seconds. An example includes KardiaMobile, a single-lead FDA-cleared medical-grade EKG-generating device. Its six-lead version is also available.
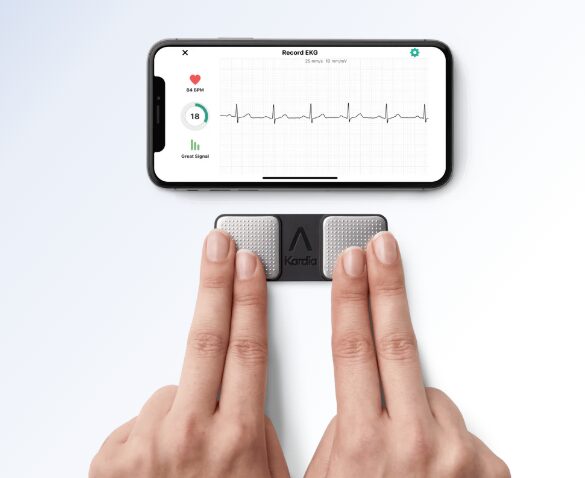
KardiaMobile (Source)
Smart therapeutic devices
Sleep assistance devices
While several monitoring devices assess sleep quality, some actively improve it. One example is Pod4 from EightSleep. It regulates the bed’s temperature while you sleep to match your body’s natural rhythm, keeping you in deep sleep for longer. It can also adjust the bed’s elevation to improve breathing and mitigate snoring.

Pod4 (Source)
Another device, Embr Wave from EmbrLabs, generates cool or warm sensations inside your wrist at the touch of a button. This triggers a natural mind-body comfort response that helps relieve sleep, hot flashes, stress, and more. It is beneficial for women in menopause.
Tremor therapy
People with essential tremors or Parkinson’s can benefit from IoT devices that provide personalized therapy. Cala Klq, an FDA-cleared wearable by Cala Health, is one such device that notes the patient’s tremor signature and provides a 40-minute personalized therapy session. After the session, patients typically experience relief for more than an hour.

Cala KLQ (Source)
Another competing product is Allevx from Allevion Therapeutics, which uses a patented wearable to deliver a 20-minute therapy session. Encora Therapeutics has also created another similar device.
Pose correction devices
Several physiotherapy patients are victims of incorrect poses triggered by an unergonomic sedentary lifestyle or incorrect poses during exercising or workouts. Pose correction devices help the user become mindful of an incorrect pose. Some examples of such devices are given below:
GO2 by Upright attaches to the back of your neck, calibrates your upright pose after the first installation and vibrates whenever it detects slouching. The intensity and frequency of the vibrations can be controlled using the mobile app.

Upright GO2 (Source)
Yoga Pants by Wearable X are pants with attached sensors and haptic feedback (vibration) to detect and improve Yoga poses. You can choose your workouts from the app, configure the vibration intensity, and track daily progress.

Tech-enabled Yoga (Source)
Smart hearing aids
Traditional hearing aids are now replaced with smarter alternatives that allow users to adjust their settings using a mobile app. Examples include ‘music mode’ for better hearing live music or customizations for noise cancellation during one-on-one conversations. An example of a hearing aid is Enhance Select 500 by Jabra.

Jabra Enhance Select 500 (Source)
Smart hospital equipment
Robotic surgery
Ultra-high precision surgery with minimal human intervention is now possible thanks to advancements over the past several decades. Innovation in this space focuses on
- Making the experience more immersive for surgeons.
- Reducing the force on patient tissues.
- Building capabilities to enable more kinds of surgeries.
- Reducing surgery time.
- Providing more real-time feedback to surgeons.
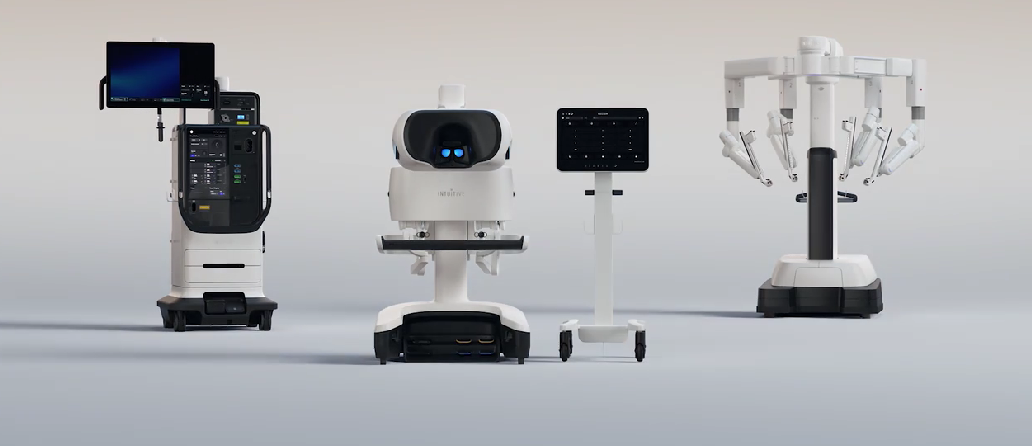

Da Vinci 5 (Source)
Several companies are working in this space, and one of the most popular product is Da Vinci 5 from Intuitive Surgicals. The platform enables minimally invasive surgery across several specialties, including urology, gynecology, general surgery, and thoracic surgery. Surgeons direct the arms for higher precision and zoom.
Smart beds and accessories
Smart hospital beds are designed to increase patient safety, monitor them continuously, and improve communication with healthcare providers.
For example, Centrella Smart+ Beds feature innovations such as motion-activated nightlights, comfortable therapeutic surfaces, and continued patient monitoring. They also come with an enhanced 3-mode bed exit system that helps reduce falls and related injuries. Using an integrated sensor in the bed frame, they can measure heart and respiratory rates and alert healthcare providers if these rates cross a customizable threshold.
Centrella Smart+ Bed (source)
Smart IV pumps with built-in drug libraries and dose error reduction systems (DERS) are an auxiliary device category to smart beds. Once users input the desired medication and patient information, they automatically calculate the infusion rates and alert care providers if the infusion rate exceeds acceptable dosing limits.
Some examples of companies making smart infusion pumps include B Bruan, Med One Group, and Baxter. As per various estimates, smart IV pumps are the most common hospital IoT devices.
Smart imaging systems
Smart MRI, X-ray, and CT scan machines can upload images directly to the cloud and transfer them to physicians’ phones or computers within seconds, supporting remote diagnosis and consultation. Examples include Waldent’s Smart DC Portable X-ray machine (made for dental X-rays). It also harnesses AI to reduce scan times, enhance image quality, and improve patient comfort. You can read more here.
Smart imaging systems are not just restricted to equipment. Innovations like Sony’s NUCLeUS allow for better imaging in the Operating Room and transmit still images or video feeds across the hospital network. This can allow surgery to be monitored remotely (helping university hospitals) or attach still images from the surgery to the patient’s medical records.
Physical security equipment
CCTV cameras, biometric and RFID access, visitor management, inventory control, alarm, and edge analytics systems ensure safe and efficient medical operations. Most hospitals have different vendors. For example:
- Axis, Hanwha, Bosch, and Avigilon for CCTV cameras,
- Mercury, AMAG, and Honeywell for access control systems,
- Genetec and Milestone for Video Management Systems (VMS).
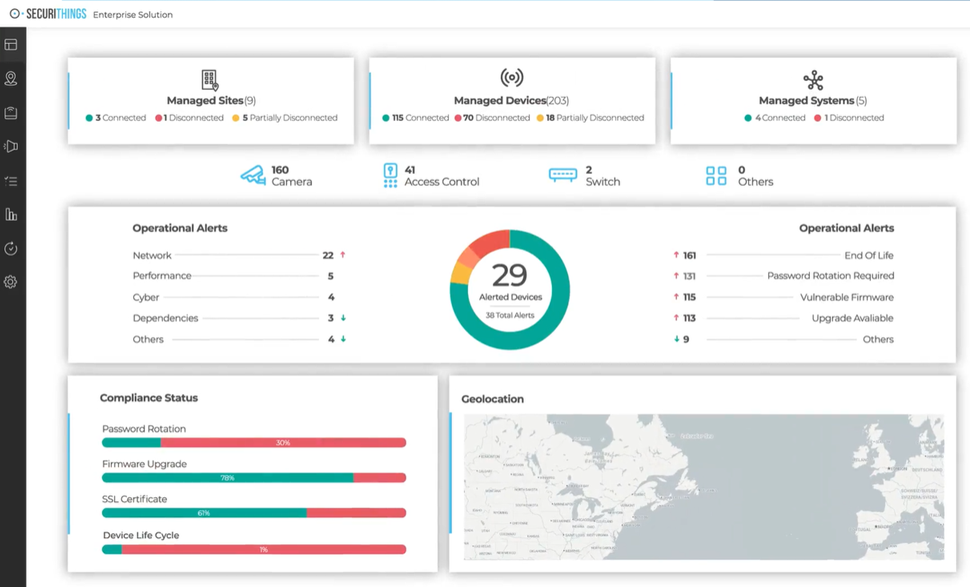
As your physical security infrastructure scales, an enterprise physical security platform like SecuriThings becomes necessary. It performs centralized device discovery, lifecycle management, password rotation, firmware upgrades, and compliance reporting. Learn more about the application of SecuriThings in the healthcare industry and hospital environments.
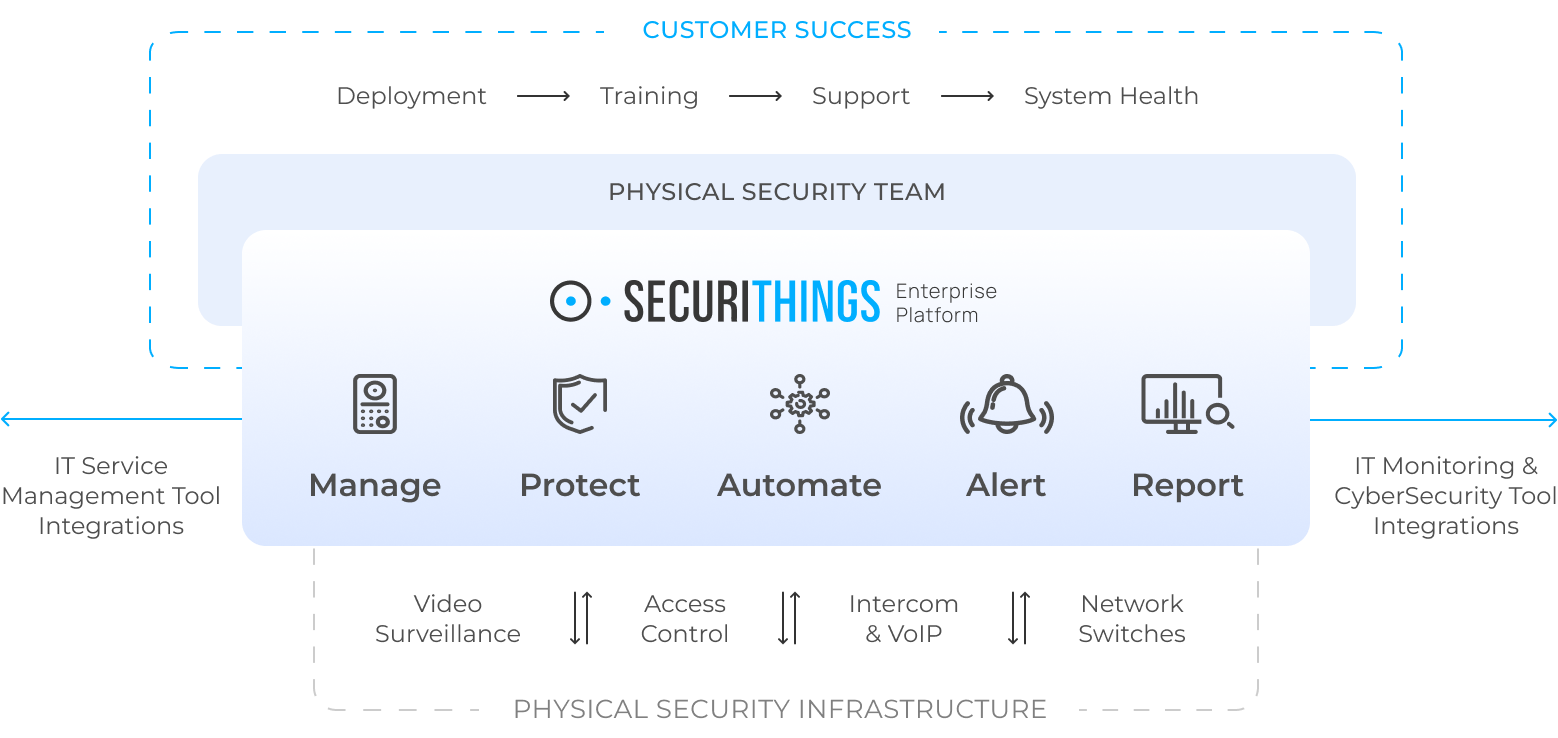
SecuriThings physical security management solution (Source)
Healthcare IoT device vulnerabilities
Healthcare IoT devices often suffer from the same vulnerabilities that generally affect IoT devices. Exploiting vulnerabilities can result in overcharging, increased hospital stays, and, in the worst-case scenario, a patient’s death.
Hardcoded credentials
Several devices use hardcoded credentials that, if not changed by the users, can provide a pathway for malicious actors to access the systems. Ideally, a device should force the users to change the password at the time of setup.
CVE-2022-22765, found in certain patient monitoring systems, allowed threat actors to use hardcoded credentials to access, modify, or delete sensitive information, including protected health and personally identifiable information.
Exposure to sensitive information
Unencrypted communication between the system and the application or between different components of the system can expose sensitive information to malicious actors.
CVE-2020-25179 found in GE Healthcare Imaging and Ultrasound products allowed specific credentials to be exposed during transport over the network. Another example is CVE-2021-42744 found in Philips MRI 1.5T and 3T Version 5.x.x.
Application vulnerabilities
Each IoT device typically has a user application, either on the mobile phone or the desktop. These applications are also prone to vulnerabilities that can provide access or leak sensitive information to hackers.
CVE-2022-26392 affected the Baxter Spectrum infusion system’s Wireless Battery Module (WBM). In superuser mode, the WBM was susceptible to format string attacks via application messaging. The attacker could then read the WBM’s memory to access sensitive information.
Improper or missing authentication
If a device has weak password policies, or pathways that do not check for authentication, then hackers can exploit these vulnerabilities to access the devices.
CVE-2019-6538 affected several monitor versions of Medtronic’s implantable cardiac devices, allowing an attacker with adjacent short-range access to an affected product. The attacker could then replay, inject, modify, or intercept the data within the telemetry communication.
Path traversal
This vulnerability allows an attacker to traverse directories of the device’s file system, potentially accessing sensitive files. Attackers typically exploit the path access using the ‘./’ or ‘../’ notation.
CVE-2024-1629 is a path traversal vulnerability found in the “deleteFiles” function of Common Service Desktop, a GE HealthCare ultrasound device component. This vulnerability allowed attackers to access directories they did not have access to.
SQL injection
If an application doesn’t perform checks on input data sent by users, a threat actor could send a malicious SQL script like ‘DELETE * from table’ to compromise the availability, confidentiality, or integrity of data.
CVE-2021-39375 affected Philips Healthcare Tasy Electronic Medical Record (EMR) 3.06, allowing SQL injection via the WAdvancedFilter/getDimensionItemsByCode FilterValue parameter
Buffer overflow
If a device’s firmware doesn’t perform validation on input data’s length, it can lead to out-of-bounds memory operations and downtimes.
CVE-2021-37166 was discovered in the Swisslog Healthcare Nexus Panel’s HMI3 Control Panel, resulting in a denial of service.
These vulnerabilities are not specific to healthcare IoT. Therefore, the best practices for protecting yourself against these vulnerabilities also include common guidelines that apply to IoT devices in general.
Best practices in healthcare IoT management
To better protect yourself against the vulnerabilities present in healthcare IoT devices, follow these best practices:
Firmware updates
A firmware upgrade typically fixes any detected or reported vulnerability. Please ensure you download and apply the update as soon as it is available. If you have multiple devices within an organization, it is best to offload firmware upgrades to an enterprise management solution like SecuriThings.
Password policies
Change the default password immediately and use a strong password across all devices and associated applications. The password should be rotated periodically. Multi-factor authentication should be used based on the availability and criticality of the application.
Data sharing
Always consult your physician or hospital before allowing anyone to gain access to the data generated by your smart device. If you are managing healthcare IoT devices in an organization (like a hospital), make sure that there are strict access-control rules in place, following the principle of least privilege.
Compliance
Before purchasing a smart device, check for compliance with locally applicable regulations. Examples of these regulations are HIPAA and GDPR. Adherence to these regulations ensures some level of security and privacy. It also helps with the interoperability of devices, which is useful when we want devices from different manufacturers to operate seamlessly within a system.
Enterprise management
If you run a hospital or any establishment that requires many healthcare IoT devices, consider deploying an enterprise-level device management solution like SecuriThings that offloads device discovery, firmware updates, compliance adherence, and threat intelligence.
Conclusion
IoT devices in healthcare are available to personalize and improve patient life experience, speed up recovery, and provide a holistic view of patient vitals for specialized treatments or medical diagnosis. While they aren’t immune to the vulnerabilities found in generic IoT devices, proper adherence to best practices minimizes adverse impact.