Free educational articles for physical security professionals.
Physical security controls protect an enterprise’s assets, personnel, and infrastructure from physical threats, including unauthorized access, theft, vandalism, and natural disasters. These controls are structured in layers and range from deterrent and preventive to compensatory and recovery, ensuring the security of digital and physical assets. They are essential to strengthening an organization’s physical security cybersecurity and provide a fundamental deterrent to threat actors. Implementing suitable physical security controls is vital to achieving robustness in financial institutions, government offices, residential areas, shopping centers, and commercial building security systems.
This article examines nine categories of physical security controls. It discusses the systems and technologies that implement these controls and their application in various environments. It also outlines best practices for implementing these controls. The article aims to ensure that organizations have a solid and effective physical security structure.
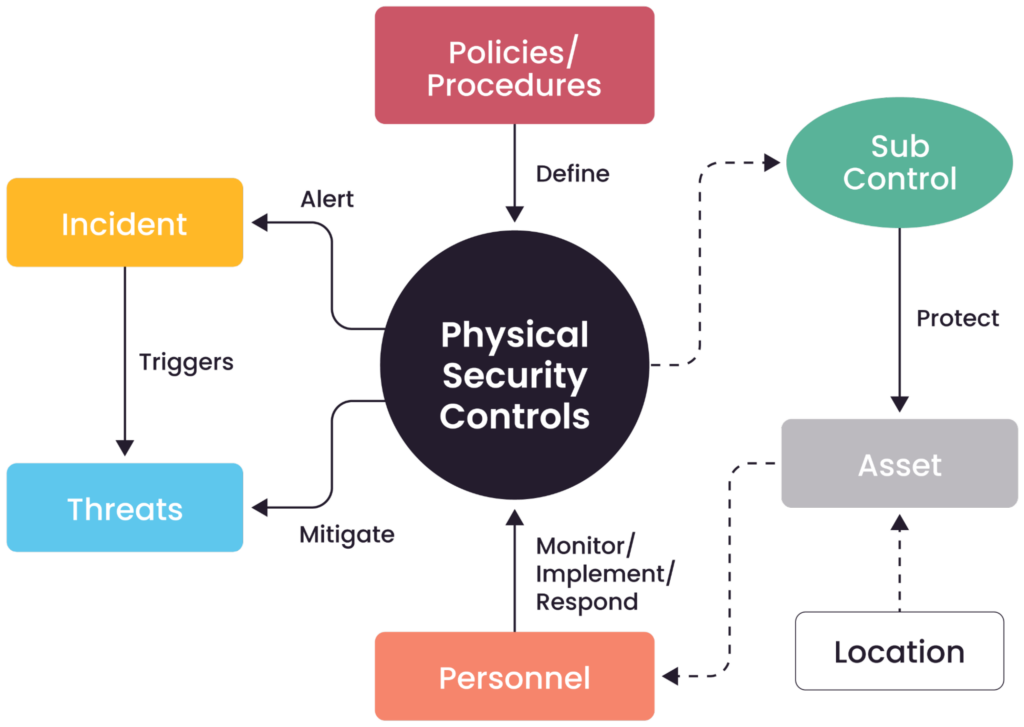
A logical overview of the relationships among physical security controls, assets, personnel, threats, and incidents
Monitor the health of physical security devices and receive alerts in real-time
Automate firmware upgrades, password rotations & certificate management
Generate ad hoc and scheduled compliance reports
| Control category | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Deterrent controls | Discourage potential attackers or unauthorized access by creating a perception of security presence |
| Preventive controls | Physically block or mitigate unauthorized access before a threat can materialize |
| Detective controls | Identify and alert about unauthorized or suspicious activity in real-time |
| Corrective controls | Respond to and mitigate the damage of security incidents after they have occurred |
| Compensatory controls | Provide alternative protection in scenarios where primary controls are inadequate or detective controls indicate an ongoing security breach |
| Recovery controls | Help recover assets or operations following a breach or disaster; these are forms of disaster recovery plans and business continuity plans |
| Environmental Controls | Guard against environmental threats such as fire, flooding, or extreme weather |
| Cyber-physical controls | Manage and monitor interactions between digital systems and physical security systems, ensuring the security and optimal performance of operational technology and information technology devices |
| Administrative controls | Manage and enforce the proper implementation of physical security by guiding personnel behavior and decision-making |
Deterrent controls discourage potential attackers by creating a visible security presence; they focus on instilling a risk perception in those considering unauthorized actions. These controls are implemented to reduce the likelihood of security violations. Here are some examples:
Preventive controls form the first line of defense by physically preventing unauthorized access and mitigating potential security threats before they materialize. These controls include physical barriers, lighting systems, and access control technologies.
Take security locks, for instance: a key element of preventive controls. These locks incorporate mechanisms to resist tampering and picking. Mechanical locks offer reliability, while electronic locks improve security with fail-secure strike locks (which remain locked during power interruptions) and fail-safe magnetic locks (which unlock in emergencies to ensure safe egress).
The diagram below illustrates how these mechanisms operate during power interruptions.
A diagram of the controls of electronic locking mechanisms during power interruptions
Equally critical are access control systems, which regulate entry and exit into restricted zones and monitor and log activities for security audits. These systems include:
Other preventive controls include turnstiles, vestibules, and security gates, which are pivotal in regulating and monitoring the movement of individuals entering and exiting a facility. Electric fencing provides a deterrent barrier at facilities’ perimeters by delivering a high-voltage electric current along the fence line. For the secure storage of sensitive documents, valuables, and equipment, safes and vaults offer preventive control, with some offering features such as a multiuser-dependent “bank mode” and dispatch-center-reliant interactive code systems to ensure proper access controls.
A good physical security design prioritizes technologies and systems that detect and alert security teams about unauthorized access or suspicious activity. If well implemented, detective controls identify and expose potential intruders or attackers as they attempt to gather information on accessing the premises.
Here are standard detective controls ordered by ease of implementation, effectiveness, and applicability in commercial building security systems:
A functional block diagram illustrating video analytics and the associated controls.
These controls react to security breaches and incidents, stopping or mitigating damage after it occurs. They include:
These measures provide an alternative solution to enhance security when primary controls (deterrence, detective, and corrective) fail or are insufficient. A common practice is manual security checks, which involve dispatching response crews to premises with reported alarm signals. Central monitoring systems are crucial in these response controls, as they receive alarms and intelligent CCTV alerts.
Additionally, temporary controls are implemented in access control systems to enforce the fail-secure protocol during system outages. This protocol ensures the automatic closure of all entry points when the server is offline and edge devices, such as readers, cannot retrieve access-level data, effectively blocking unauthorized access while maintaining security.
Recovery controls are measures implemented with physical security systems to restore operations or facilities after a security breach or disaster. There are two common recovery controls applied in physical security:
These controls safeguard facilities and assets from environmental hazards like natural disasters and extreme conditions. These systems protect against fire, flooding, gas leaks, or extreme weather. They include the following:
These measures and systems manage and monitor interactions between digital and physical security systems, ensuring safety, security, and functionality.
Cyber-physical controls include:
Physical security management software protects the attack surface created by physical protection systems connected to the network, like IP cameras and physical access control devices. SecuriThings offers the industry’s most comprehensive physical security management software, which covers the lifecycle of physical device management with features such as maintaining inventory, installing operating systems patches, rotating passwords, and generating regulatory compliance reports.
These involve policies, procedures, and measures that govern the implementation and management of physical security. These controls ensure that physical security measures are correctly applied, maintained, and aligned with an organization’s risk management strategies:
The table below describes the application environments of the various control categories discussed above and examples of relevant systems.
| Control category | Application environment | Examples of systems |
|---|---|---|
| Deterrent | Office buildings, malls, schools | Electric fences, warning signs, perimeter lighting, guards |
| Preventive | Banks, government offices, data centers | Security locks, access control systems, biometric systems, electric fencing |
| Detective | Embassies, military bases, high-security corporate buildings | Surveillance systems, motion detectors, intrusion detection systems, virtual fencing |
| Corrective | Data centers, hospitals, large corporate establishments | Fire suppression systems, backup batteries, emergency exit systems |
| Compensatory | Airports, financial institutions, telecom facilities | Manual security checks, temporary access controls, fail-secure protocols |
| Recovery | Financial institutions, cloud
service providers, data centers |
Data recovery systems, system replications, business continuity plans |
| Environmental | Data centers, labs, server rooms | Uninterruptible power supplies (UPS), fire suppression systems, HVAC systems |
| Cyber-physical | Industrial facilities, smart buildings, airports | Security information and event management systems, network segmentation, visitor management systems, physical security management software |
| Administrative | Corporate offices, government institutions | Security policies, training programs, incident response plans |
Physical security threats are ever-evolving, placing greater responsibility on engineers to implement robust systems that wholesomely protect an establishment. The layered approach to physical security controls spanning deterrent, preventive, corrective, and recovery measures ensures comprehensive protection across various environments.
To enhance these efforts, integrating innovative platforms like SecuriThings can revolutionize the management of physical security controls by automating device hardening, ensuring compliance, and minimizing cyber risks. For engineers, adopting such innovative platforms is an enhancement and a necessity to future-proof infrastructure against emerging threats. Take the next step: Optimize your security systems.
