Commercial Building Security Systems
- Chapter 1: Tutorial & Best Practices
- Chapter 2: Commercial Building Security Systems
- Chapter 3: Physical Security Systems
- Chapter 4: Data Center Physical Security
- Chapter 5: Physical Security Cybersecurity
- Chapter 6: Physical Security Plan
- Chapter 7: Physical Security Controls
- Chapter 8: Retail Security Systems
- Chapter 9: Physical Security Tools
- Chapter 10: Physical Security Program Best Practices
- Chapter 11: Physical Security Policy Best Practices
- Chapter 12: Best Practices for Physical Security and Cybersecurity
- Chapter 13: Best Practices for Corporate Physical Security
- Chapter 14: Physical Security Best Practices
- Chapter 15: How physical security powers
- Chapter 15: Best Practices for Physical Security Devices
Commercial building security systems have evolved from traditional mechanical locks and guards to advanced technology-driven solutions. Modern commercial building security systems enable predictive analytics, timely anomaly detection, and seamless device communication to address the new wave of cybersecurity threats.
As the industry has matured, market demand, competition, and industry standards have led to a combination of comprehensive technologies and building security practices organizations can use to protect their assets.
This article will discuss the modern security systems suitable for commercial buildings and the critical factors to consider when selecting them, with an emphasis on the importance of exception-driven monitoring, cloud storage, and video verification. It will provide guidance on how to optimize commercial building security systems and leverage existing IT infrastructure.
Summary of key commercial building security systems features
The nine main features and technologies a reliable commercial building security system should have based on the application scenario are summarized in the table below.
| Desired Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Intrusion detection | The use of various sensors and technologies for detecting and reporting intrusion. |
| Video surveillance | Cameras and advanced video analytics are used to detect, alert, and record suspicious activity. |
| Advanced Access Control | Technologies for managing and monitoring access to restricted areas using biometric authentication, smart cards, and remote management. |
| Integration Capabilities | Ability to integrate with other building management and IT systems. |
| Centralized Management | Unified interface for monitoring and controlling all security devices. |
| Stability and Resilience | Ability to scale with building or security needs, have high availability with redundancy and provide real-time monitoring of devices. |
| Data Analytics | Use of data to optimize security operations and predict potential threats. |
| Compliance with Standards | Adherence to industry standards and regulations for security systems. |
| Cybersecurity Measures | Protection against cyber threats targeting physical security devices. |
Nine essential commercial building security system features
The sections below will explore the nine essential commercial building security features.
Intrusion detection
Commercial buildings have intrusion detection systems (IDS) to detect and report intrusions during non-business hours. The common types of sensors used in an IDS include:
- Motion sensors: These use passive infrared (PIR), ultrasonic, and microwave technologies, often combined in dual-tech and tri-tech configurations, to detect motion.
- Contact-based sensors: Use reed switches to monitor the opening and closing of entry and exit points, such as doors and windows.
- Vibration/shock sensors: Use piezoelectric materials to sense vibrations or mechanical stress, detecting potential tampering or forced entry.
- Glass break detectors: Detect the sound and vibrations associated with breaking glass, providing an early warning of potential breaches.
These sensors use an alarm panel to detect, interpret, and report suspicious activities.
Video surveillance
Technological advancements have led to sophisticated CCTV systems that enable proactive rather than reactive monitoring. Modern systems generate alerts for exceptions such as unattended baggage, blacklisted individuals, and the presence of weapons, promptly notifying security personnel. Key technologies used in these systems include:
- Automatic Number Plate Recognition (ANPR): This is used in applications requiring rapid vehicle identification and monitoring. ANPR uses advanced image processing and ML to capture and analyze vehicle plates. A cloud-based IoT management platform will enhance real-time monitoring across various security systems.
- Facial recognition: Uses image processing and AI to enable seamless monitoring and intelligent search.
- People counting: Systems that use advanced video analytics within CCTV to track and quantify foot traffic by detecting, identifying, and distinguishing individuals in real time. It is used in various business premises for security and operational optimization.
- Intrusion detection: Predefined zones with a set minimum and maximum target size, time threshold, and sensitivity can detect unauthorized movement or activity.
- Region entrance and exit monitoring: Using analytics and alerts to track the movement of personnel and vehicles into and out of designated zones.
- Line crossing detection: Using virtual boundaries to trigger an alert when an object crosses a set direction. This is predominantly used for perimeter protection.
- Behavior analytics: Automates the detection of suspicious activities by analyzing patterns in real-time video feeds.
The features discussed can be applied in various scenarios in commercial buildings to enhance the efficiency and effectiveness of video surveillance.
-

Monitor the health of physical security devices and receive alerts in real-time
-

Automate firmware upgrades, password rotations & certificate management
-

Generate ad hoc and scheduled compliance reports
Advanced access control
Access control systems control, monitor, and log access into and out of restricted areas. They can be categorized into human and vehicular access control. Both categories can have a supplementary security measure that introduces the ability to manage and verify entry into a restricted area. The supplementary security measures are intercom and visitor management.
Vehicular access control
These have evolved significantly with advancements in physical security technologies. Automated boom barriers, often integrated with RFID readers, license plate recognition (LPR), or access cards, efficiently control vehicle entry and exit. Barrier gates, designed to withstand impact, are typically used at high-security locations and are integrated with access credentials for secure entry. Retractable or fixed bollards prevent unauthorized vehicle access and are controlled via remote systems or integrated with access control platforms. Recent advancements have introduced IP-based vehicular access control devices, allowing them to be managed, monitored, and controlled on a CMS via the IT infrastructure.
Human access control
Facial recognition technology provides a contactless biometric solution that scans and verifies facial features to grant or deny access. Iris reading is another advanced biometric solution that scans the unique patterns in a person’s iris for authentication. Fingerprint scanning remains a standard biometric method that uses unique fingerprint patterns to authenticate users. Additionally, other biometric technologies, including voice recognition, palm vein scanning, and multimodal biometrics, offer diverse options for securing human access to commercial buildings.
Intercom and visitor management
These systems facilitate communication between entry points and security personnel or tenants. Video and audio intercoms, now often IP-based, are integrated with visitor management systems to register and track visitors efficiently. Their integration with cloud-based platforms allows for remote opening of doors and gates from mobile devices, enhancing convenience and security.
Centralized management
Deploying a central management system (CMS) in commercial buildings is critical to ensuring interoperability among individual components such as IDS, CCTV, fire alarms, and access control systems. The CMS uses analytics to provide features like device health monitoring, batch configurations, and firmware upgrades, ensuring seamless integration and efficient management of all security components.
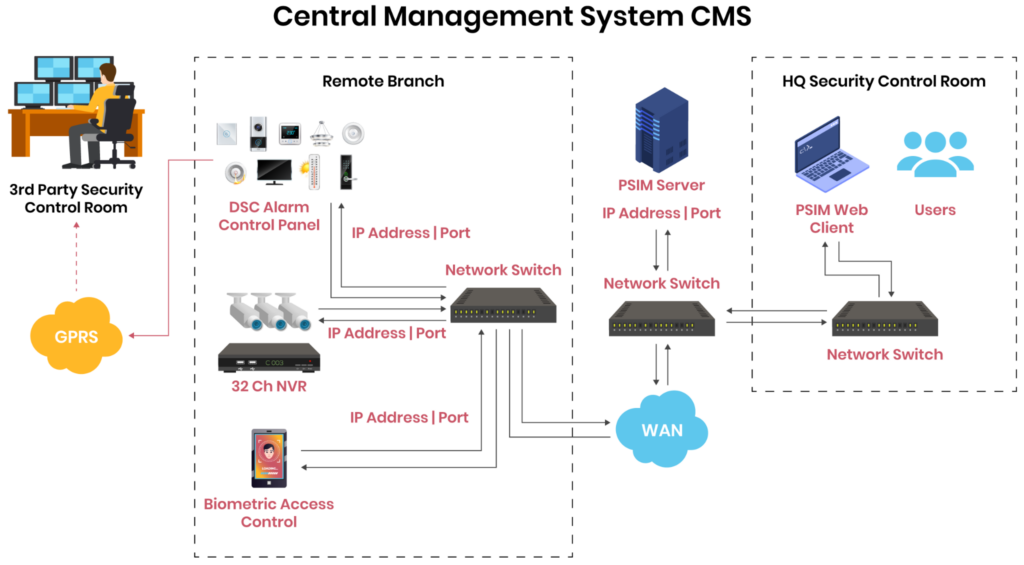
A logical overview of a commercial building security system CMS.
In the context of CMS for commercial building security systems, SecuriThings provides a centralized platform for automating and securing physical security devices at scale, ensuring real-time operational efficiency and robust cybersecurity. The platform offers features such as:
- Real-time availability monitoring: This feature allows security personnel and technical teams to be aware of the status and performance of each device. SecuriThings Enterprise Solution can identify operational issues and downtimes for cameras, alarm system sensors, and access control devices and promptly alert the Physical security teams.
- Smart alerts & analytics: Using advanced analytics, the platform can analyze device behaviors and security activities and flag anomalies such as unauthorized access attempts, malfunctioning devices, and unusual activities. This can help preempt potential system vulnerabilities.
- Automated device operations: SecuriThings automates routine activities such as firmware updates, device configuration, and security patches and reduces the need for manual intervention.
- Cybersecurity protection: a good CMS should encrypt data both in transit and at rest, use multi-factor authentication for secure access, and segment security devices from IT and network infrastructure.
Stability and resilience
The deployment of a commercial building security system must be able to accommodate growing requirements, include redundancy for reporting and connectivity, and enable remote monitoring of device health statuses.
Scalability
The security systems should be able to grow and adapt to increasing demands by using modular components like cameras and sensors, integrating with existing IT infrastructure, and utilizing distributed processing and cloud-based solutions. They ensure performance and reliability through seamless integration, flexible configurations, and robust network protocols like ONVIF, RTSP, and BACnet, which support evolving security needs and handle large data volumes and complex analytics.
Reliability and redundancy
This involves implementing robust failover mechanisms and backup solutions to maintain operational integrity in the event of component failures. Systems should include dual power supplies, redundant communication paths, and fail-safe modes for critical components like alarm panels and cameras. Additionally, data should be regularly backed up to secure, remote locations, preferably cloud-based servers, to prevent loss from hardware malfunctions or cyber incidents. Designing for high availability with these redundancy features minimizes downtime and maintains consistent security coverage, even during system maintenance or unexpected failures.
Health monitoring
Health monitoring supports system reliability and optimal operation, allowing users to identify and address potential issues proactively. Modern security systems utilize existing internet infrastructure within commercial premises to enable remote health monitoring. One of the key features of health monitoring is the presence of tools for managing firmware and software updates to keep devices secure and up to date.
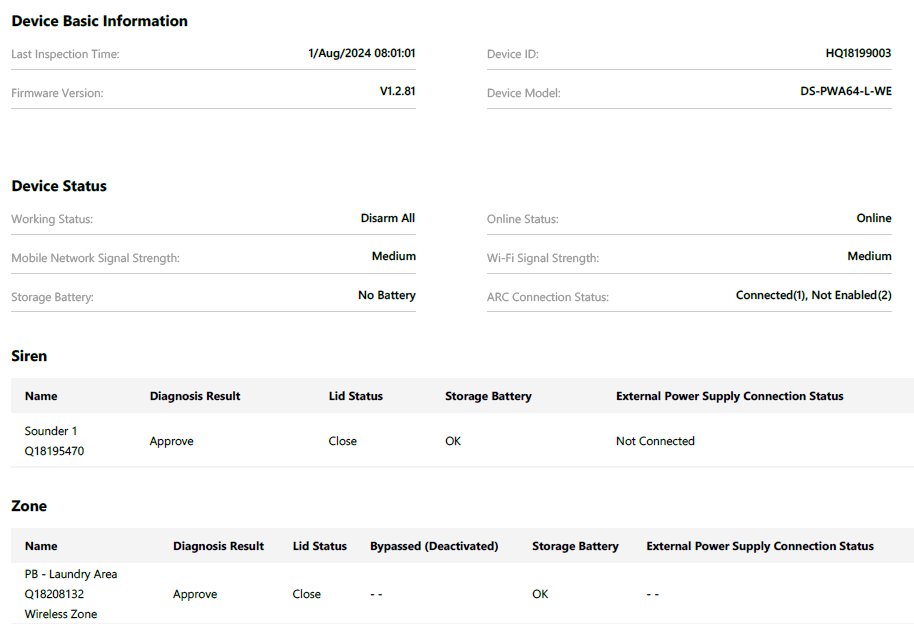
Health monitoring for building security devices.
Integration capabilities
Integration with building management systems, IT infrastructure, and other security systems is important for seamless operation. Physical Security Interoperability Alliance (PSIA) allows unidirectional data flow between IP-enabled security devices, enabling functionalities such as:
- Infrastructure Video as a Service (IVaaS): a cloud-based video surveillance solution enabling security personnel to verify alarms visually before dispatching response teams. It integrates video surveillance with alarm systems to enhance response efficiency.
- Access control door release in emergencies: This system is designed to ensure egress during emergencies such as fire. The doors are operated via electromagnetic or electric strike locks controlled by relays or fire alarm panels.
- Lighting control and automation: This is based on occupancy as determined by the access control system or, in other instances, schedules based on real-time data from security sensors.
- Elevator automation: typically uses key cards, biometrics, and PIN codes to restrict access to specific floors. This integration ensures strict control and monitoring of movement within the building.
This feature enhances overall efficiency and responsiveness in commercial building security.
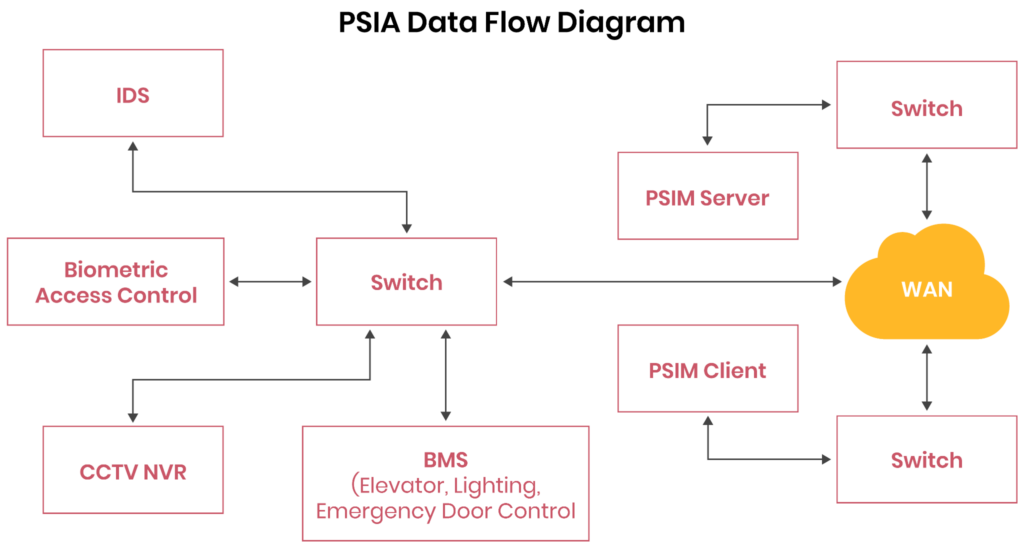
A logical overview of Physical Security Interoperability Alliance (PSIA) data flow.
Data analytics
The systems should make use of the collected data to enhance operational efficiency and predict potential threats. These analytics can identify anomalies, predict suspicious activities, and optimize response protocols by looking at patterns in video surveillance, access logs, and intrusion detection systems. This process assists in improving security measures, reducing the time spent on incident response, and adapting to evolving security needs. Advanced data analytics are necessary to proactively implement threat management and system performance optimization.
Compliance with standards
Ensuring adherence to established standards, such as ISO/IEC 27001 for information security and local fire and safety codes, guarantees that the security system can safeguard the confidentiality and integrity of sensitive data and physical assets. It involves implementing best practices for system design, maintenance, and operation and regular audits and updates to align with evolving regulations and industry benchmarks. This compliance supports system integrity, facilitates seamless integration with other building management systems, and ensures operational consistency.
Cybersecurity measures
Modern commercial building security systems must help organizations address cybersecurity risks. Here are seven security measures that commercial building security systems should provide:
- Strong encryption for data in transit and at rest: Cleartext protocols make it easier for attackers to sniff packets and capture sensitive data. Security systems should use encrypted protocols (e.g., HTTPS, TLS 1.2 and 1.3) to reduce the risk of data leakage. Similarly, encrypting data at rest reduces the risk of sensitive data exposure even if a threat actor breaches a system.
- Multi-factor (MFA) authentication for system access: Implementing MFA can significantly reduce the risk of security device compromise. Organizations should enforce MFA for connected security devices wherever practical.
- Network segmentation: Strong network segmentation can reduce attacker east-west movement in the event of a breach, help enforce the principle of least privilege, and decrease the chances of an IT network compromise leading to a compromise of security systems.
- Regular update firmware: Firmware updates may include critical security patches for vulnerabilities threat actors target. Given that many attacks on “smart” devices attempt to exploit known vulnerabilities applying firmware patches can reduce the risk of a breach. For example, many camera vulnerabilities that can be addressed with a firmware patch.
- Vulnerability assessments: Regular vulnerability assessments enable organizations to detect and address cybersecurity issues that can emerge over time.
- Threat detection: Intrusion prevention functionality can help detect threats and enable incident response for unauthorized access.
- Access logs: Unusual access attempts are a key indicator of potential attacks. Monitoring access logs for anomalies can help teams stay a step ahead of an attacker or perform root cause analysis in the event of a breach.
Conclusion
The development of commercial building security systems, from basic mechanical locks to sophisticated, technology-driven frameworks, has significantly impacted the solutions available. Modern systems leverage AI and IoT to enhance anomaly detection and reduce incident response times while maintaining a strong focus on cybersecurity. Key systems such as intelligent video surveillance, advanced intrusion detection, and smart access control are crucial for safeguarding commercial properties.
Centralized control, remote access capabilities, and scalable solutions support effective security management. Adherence to stringent cybersecurity protocols and industry standards further fortifies these systems. Security experts can ensure a robust, adaptable, and efficient security infrastructure by implementing these practices.